Hey there! Today, I want to speak about something critical for every body into fitness or dealing with diabetes: the “Blood Glucose vs Time Graph Exercise.” This tool is vital for know-how how our our bodies react to physical hobby and its effect on blood sugar.
Blood glucose vs time graphs visually display how glucose ranges change for the duration of different activities, particularly exercising, which is important for the ones coping with diabetes or aiming to stay healthy.
Key Points
- Blood glucose vs time graphs illustrate how exercising impacts blood sugar degrees.
- Understanding those graphs can help me optimize my exercise workouts and dietary selections.
- Monitoring glucose levels during exercising is crucial for safety and performance.
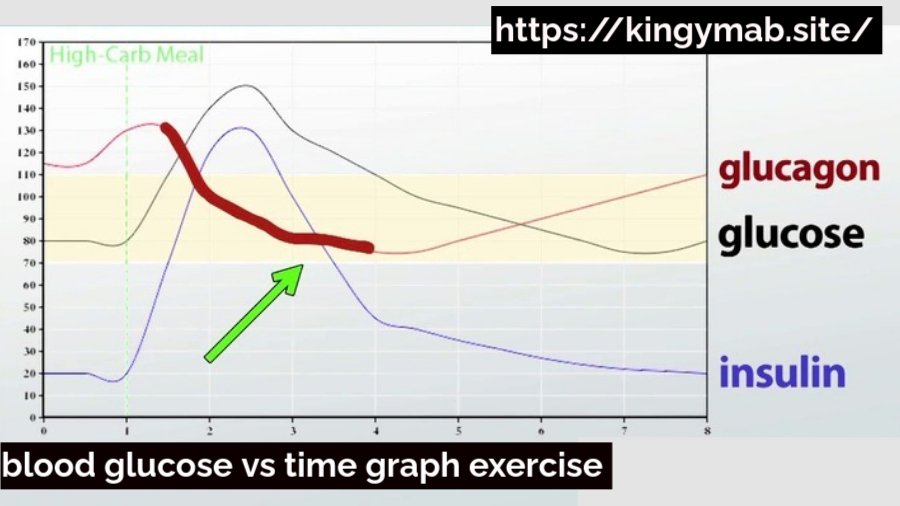
What Is a Blood Glucose vs Time Graph?
So, what exactly is this graph? It’s pretty easy!
- Structure: The x-axis usually represents time, at the same time as the y-axis suggests blood glucose awareness (measured in mg/dL or mmol/L).
- Purpose: These graphs are vital for tracking how my blood sugar adjustments in response to meals consumption and physical activity.
The Impact of Exercise on Blood Glucose Levels
Exercise has a massive effect on how our bodies control glucose.
- Physiological Response: When I work out, my muscular tissues want extra electricity, which they get from glucose. This results in increased insulin release from my pancreas, helping lower my blood sugar degrees.
- Short-time period vs. Long-time period Effects: In the quick time period, exercise can cause instantaneous drops in blood sugar. Over time, regular bodily interest improves insulin sensitivity, which allows me maintain better control of my blood glucose tiers.
Types of Exercises and Their Effects on Blood Glucose
Different styles of physical games will have numerous consequences on my blood sugar stages.
| Type of Exercise | Effect on Blood Sugar Levels |
| Aerobic Exercises | Typically, lower blood sugar significantly during and after workouts |
| Anaerobic Exercises | May cause temporary spikes due to energy demands but improve overall control with regular training |
- Aerobic Exercises: Activities like strolling or biking generally decrease my blood sugar levels drastically for the duration of and after workout routines.
- Anaerobic Exercises: Weightlifting or sprinting may purpose brief spikes in glucose because of increased power needs but can result in better ordinary manage when accomplished often.
Interpreting Blood Glucose vs Time Graphs During Exercise
Understanding how to examine these graphs is important for powerful diabetes management.
- Identifying Patterns: I look for developments in my glucose fluctuations at some stage in extraordinary workout routines. For instance, I might be aware that strolling lowers my stages extra than weightlifting.
- Safe Ranges: I intention for a pre-workout blood sugar stage among a hundred mg/dL and 250 mg/dL. Knowing my secure stages helps prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) at some stage in exercises.
Pre-Exercise Blood Sugar Management
Getting my blood sugar proper before workout is fundamental!
- Recommended Targets: Before conducting physical activity, I try and have a stable glucose degree. If it’s too low (below 70 mg/dL), I recollect having a brief snack.
- Dietary Considerations: Eating a balanced meal with carbohydrates, protein, and healthful fat about 1-2 hours earlier than exercising allows stabilize my ranges.
Monitoring Blood Glucose During Exercise
Keeping an eye fixed on my glucose even as running out is vital for safety.
- Recommended Devices: Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) are fantastic gear for real-time monitoring. They offer signals if my tiers drop too low or upward thrust too high at some point of exercising.
- Regular Checks: If I’m doing prolonged or severe exercises, checking my blood sugar each 30 minutes facilitates me stay inside secure limits.
Post-Exercise Blood Sugar Recovery
After exercise, understanding how my body recovers is critical.
- Typical Recovery Patterns: After a exercising, I often enjoy a drop in blood sugar accompanied with the aid of a sluggish upward thrust as my body replenishes energy stores.
- Post-exercise Nutrition: Consuming carbohydrates and protein after exercise enables stabilize my glucose ranges and aids recuperation.
Case Studies: Blood Glucose Responses to Different Exercises
Real-lifestyles examples can offer treasured insights into handling blood sugar in the course of workouts.
- Runner’s Response: A observe showed that runners regularly revel in good sized drops in glucose immediately after jogging because of elevated insulin sensitivity.
- Weightlifter’s Response: Weightlifters may additionally see initial spikes due to energy needs but often advantage from progressed normal manage with regular schooling.
The Role of Nutrition in Blood Glucose Management
Diet performs a essential position in managing glucose stages alongside exercise.
- Carbohydrate Intake: Consuming carbs before and after workout routines enables gasoline muscle groups and replenish glycogen stores.
- Choosing the Right Foods: I choose complicated carbs like whole grains and culmination that offer sustained power without causing sharp spikes in blood sugar.
The Importance of Hydration
Staying hydrated is key at some point of any workout habitual!
- Fluid Intake Recommendations: I ensure to drink water before, during, and after workout. Dehydration can cause higher blood sugar ranges as it affects insulin production and characteristic.
Psychological Factors Influencing Exercise and Blood Sugar
Mental properly-being can also impact how efficaciously I manage my glucose levels.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practices like mindfulness or yoga assist lessen stress, which undoubtedly affects blood sugar manipulate at some stage in workouts.
Technology in Monitoring Blood Glucose During Exercise
Innovations make monitoring less difficult than ever!
- Overview of Apps and Devices: Many apps now sync with CGMs to provide actual-time feedback on how workout routines have an effect on my glucose levels. This makes it less difficult to alter my habitual as wished.
Myths About Exercise and Blood Sugar Management
Let’s remedy a few not unusual misconceptions!
- Fasting Workouts: Some humans accept as true with workout on an empty belly is satisfactory for fats loss; however, this could result in hypoglycemia if now not controlled well. Always listen on your frame!

Conclusion
Understanding the “Blood Glucose vs Time Graph Exercise” is essential for coping with fitness through physical interest. Exercise has an immediate relationship with fluctuations in blood glucose tiers. Monitoring these stages before, at some point of, and after exercises facilitates maintain protection. Consulting healthcare professionals can offer personalized recommendation tailor-made to person desires.
By keeping an eye on these elements, I can experience a more fit life-style whilst effectively managing diabetes or fitness goals!
FAQs
How does workout decrease blood sugar levels?
Exercise will increase insulin sensitivity and promotes glucose uptake by using muscular tissues, leading to lower blood sugar tiers during and after hobby.
What should my blood sugar be earlier than exercise?
For maximum people, a pre-exercising blood sugar stage between 100 mg/dL and 250 mg/dL is considered safe; but, man or woman goals might also range.
Can I exercise if my blood sugar is low?
It’s commonly suggested to keep away from lively exercise in case your blood sugar is under 70 mg/dL. Consuming a brief supply of carbohydrates can assist stabilize it before undertaking bodily pastime.
How workout timing influences your blood sugar?
Exercise timing can appreciably impact blood sugar degrees. Exercising after food generally enables decrease publish-meal blood glucose, whilst exercise on an empty belly may additionally cause a drop in blood sugar.
How does blood glucose alternate all through workout?
During workout, muscle tissue use glucose for electricity, causing blood sugar tiers to drop. However, extreme exercising can on occasion briefly increase blood sugar due to pressure hormones being launched.
What is the exceptional time to exercising to decrease blood sugar?
The nice time to exercising to lower blood sugar is normally approximately 30 minutes after a meal. This helps save you submit-meal glucose spikes and makes use of the glucose out of your meal.
What is the 15 15 rule?
The 15 15 rule involves ingesting 15 grams of rapid-appearing carbohydrates and then waiting 15 mins to recheck blood sugar levels when experiencing low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
What allows decrease blood sugar at once?
Fast-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets, fruit juice, or sugary snacks can help lower blood sugar at once. Physical interest also can reduce excessive blood sugar levels fast.
What ingredients growth blood sugar without delay?
Foods excessive in easy sugars or carbohydrates, like sweet, sugary liquids, white bread, and fruit juice, can increase blood sugar straight away after intake.
What are the five worst foods for blood sugar?
The worst meals for blood sugar encompass sugary drinks, white bread, pastries, candy, and fried foods, as they are able to motive sharp glucose spikes and insulin resistance over the years.
Does caffeine boost blood sugar?
Yes, caffeine can boost blood sugar tiers in a few human beings. It can also cause temporary insulin resistance, that could motive blood glucose levels to rise after eating caffeinated drinks.
Is 2 hundred blood sugar normal after eating?
A blood sugar degree of 200 mg/dL or better after ingesting isn’t taken into consideration normal. It indicates that your frame is suffering to manage submit-meal glucose, which can be a sign of diabetes.
What is an alarming blood sugar level?
Blood sugar ranges over three hundred mg/dL can be alarming, as they could imply a danger of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or other severe headaches requiring on the spot medical attention.
What is ordinary A1C via age?
A regular A1C stage for maximum adults is beneath five.7%. However, for older adults, especially the ones over sixty five, a barely better A1C (around 7%) may be considered proper depending on ordinary health.
What is the threat area for blood sugar?
The danger quarter for blood sugar is normally beneath 70 mg/dL (hypoglycemia) or above 250 mg/dL (hyperglycemia). Both levels require short action to prevent excessive health problems.
Contact Us for Guest post submission






